How Can We Help?
Use Python with Codey
Use Python with Codey
Codey is a micropython-based robot.
Python code need to be uploaded to Codey in order to run.
Start Using Python
Start using Python by switching the programming mode from “Blocks” to “Python”

Note: please make sure that Codey is currently selected.
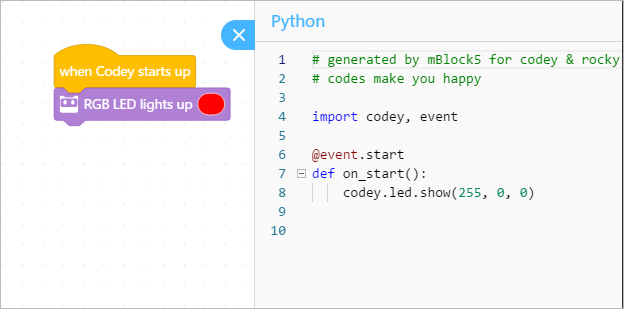
Here’s an example code:
import codey
import rocky
import time
import event
@event.start
def on_start():
codey.led.show(255,0,0)
rocky.forward(50,1)
After programming, click “Upload” to upload the program to Codey.
Convert Blocks to Python
In the Scripts area, click ![]() to covert blocks to Python. The following is an example:
to covert blocks to Python. The following is an example:
Use the Face Panel
display.show(text, wait=False)
Show a piece of text on Codey’s Face Panel.
codey.display.show(“hello world”, wait=False)
codey.display.show(3.14, wait=False)
codey.display.show(“14:02”, wait=False)
display.show_image(image, time)
Show an image on Codey’s face panel. The image displayed needs to be converted to hexadecimal data.
If the duration is any other number than zero, the panel will turn off after the set duration.
codey.display.show_image(“00003c7e7e3c000000003c7e7e3c0000”, time_s=1)
display.show_image(image, x, y)
Display an image on Codey’s face panel at a specific location (x, y).
codey.display.show_image(“000c18181c0c000000000c1c18180c00”, 0, 0)
# Show a smiley face at the upper-left corner
codey.display.set_pixel(x, y, status) / codey.display.toggle_pixel(x, y)
- set_pixel: set the status of the pixel at (x, y); set True to light up the pixel, or False to turn it off
- toggle_pixel: toggle a pixel at (x, y): turn on if it is off, and off if it is on
codey.display.set_pixel(5, 5, True) # light up the pixel at (5, 5)
codey.display.set_pixel(5, 5, False) # turn off the pixel at (5, 5)
codey.display.toggle_pixel(5, 5) # toggle the pixel at (5, 5)
display.get_pixel(x, y)
Check if the certain pixel of Codey is on or not. If on, return True; otherwise return False
print(codey.display.get_pixel(5, 5)) # print True if the pixel at (5, 5) is on
display.clear()
Clear all the contents on Codey’s face panel.
codey.display.clear() # turn off the face panel
Use the RGB LED on the Codey
led.show(r, g, b, time)
Set the color of Codey’s LED.
If the duration is a non-zero number, the LED will turn off after specified seconds.
codey.led.show(255, 255, 0, 1) # set the color, turn off after 1 second
codey.led.show(255, 0, 0) # change the color to red
led_off()
Turn off Codey’s LED.
codey.led_off() # turn off the led light
led.set_red(value) / led.set_green(value) / led.set_blue(value)
Set the RGB value of the LED independently. The range of each color value is 0-255.
codey.led.set_red(255)
codey.led.set_green(255)
codey.led.set_blue(255)
Make a Sound
speaker.play_melody(name)
Play the a sound file.
codey.speaker.play_melody(“meow”)
codey.speaker.play_melody(“meow.wav”) # .wav is optional
Sound file available:
- hello.wav : hello
- hi.wav :hi
- bye.wav : bye
- yeah.wav : yeah
- wow.wav : wow
- laugh.wav : laugh
- hum.wav : hum
- sad.wav : sad
- sigh.wav : sigh
- annoyed.wav : annoyed
- angry.wav : angry
- surprised.wav : scared
- yummy.wav : pettish
- curious.wav : curious
- embarrassed.wav : embarrassed
- ready.wav : ready
- sprint.wav : sprint
- sleepy.wav : snore
- meow.wav : meow
- start.wav : start
- switch.wav : switch
- beeps.wav : beeps
- buzzing.wav : buzz
- exhaust.wav : air-out
- explosion.wav : explosion
- gotcha.wav : gotcha
- hurt.wav : painful
- jump.wav : jump
- laser.wav : laser
- level up.wav : level-up
- low energy.wav : low-energy
- metal clash.wav : metal-clash
- prompt tone.wav : prompt-tone
- right.wav : right
- wrong.wav : wrong
- ring.wav : ringtone
- score.wav : score
- shot.wav : shot
- step_1.wav : step_1
- step_2.wav : step_2
- wake.wav : activate
- warning.wav : warning
speaker.play_note(note_number, beats)
Tell Codey to play a musical note for a duration.
The note number is the MIDI number. You may also use note names like “C3” or “D4”. Incorrect note name will produce an error in the console.
codey.speaker.play_note(36, 1)
codey.speaker.play_note(‘c3’, 0.25)
speaker.play_tone(frequency, beats)
Play a certain frequency of sound for a duration of certain beats.
codey.speaker.play_tone(700, 1)
speaker.rest(beats)
Pause the sound for a certain number of beats.
codey.speaker.rest(0.25)
speaker.stop_sounds()
Stop all sounds.
codey.speaker.stop_sounds()
speaker.volume
Set or read the volume of Codey’s speaker.
codey.speaker.volume = (70) # Set the volume of Codey’s speaker to 70%
print(codey.speaker.volume) # Get the current volume of Codey’s speaker
Use the Sensors of Codey
button_a.is_pressed()/button_b.is_pressed()/button_c.is_pressed()
If the specified button is pressed, return True; otherwise, return False.
print(codey.button_a.is_pressed()) # print True if the button A is pressed.
potentiometer.get_value()
Get the position of the potentiometer knob on Codey’s side. The value will be 0-100.
print(codey.potentiometer.get_value()) # Get the position of potentiometer
sound_sensor.get_loudness()
Get the loudness of the sound sensor. The range is 0-100.
print(codey.sound_sensor.get_loudness()) # output the loudness of the sound sensor
light_sensor.get_value()
Get the light intensity detected by the light sensor. The range is 0-100.
print(codey.light_sensor.get_value()) # output the light sensor’s value
motion_sensor.is_shaked()
Tell whether the Codey is being shaken. The result is True or False.
print(codey.motion_sensor.is_shaked()) # if Codey is being shaken, return True
motion_sensor.is_tilted_left()/motion_sensor.is_tilted_right()/
motion_sensor.is_ears_up()/motion_sensor.is_ears_down()
Tell whether Codey is tilted to the right/left, or placed ears-up/ears-down. The result is True or False.
print(codey.motion_sensor.is_tilted_left()) # If Codey is left-tilted, return True
print(codey.motion_sensor.is_ears_up()) # If Codey is placed ears-up, return True
Gyroscope
Get the roll, pitch or yaw value of Codey’s gyroscope
- motion_sensor.get_roll()
- motion_sensor.get_pitch()
- motion_sensor.get_yaw()
Get the gyroscope’s rotation value (in degrees) around a certain axis.
- motion_sensor.get_rotation(axis): x, y, or z axis
- motion_sensor.reset_rotation(axis=”all”): reset the rotation angles of the gyro
You can use motion_sensor.get_shake_strength() to get the intensity of the shaking.
print(“The yaw and pitch is:”, codey.motion_sensor.get_yaw(), codey.motion_sensor.get_pitch()) # output the yaw and pitch value of the gyro
print(“The rotation value is:”, codey.motion_sensor.get_rotation(x), codey.motion_sensor.get_rotation(y), codey.motion_sensor.get_rotation(z))
codey.motion_sensor.reset_rotation() # reset the rotation value.
print(“Shake strength:”, codey.motion_sensor.get_shake_strength())
get_timer()
Get the timer value in seconds (since startup or last reset)
print(codey.get_timer()) # print the timer value since startup or last reset
reset_timer()
Reset the timer.
codey.reset_timer()
print(codey.get_timer()) # prints 0
Codey’s Events and Flow Control
Codey supports events (like when the button is pressed), and it also supports multi-threading.
If you wish to use event, declare a function and register it to the event. A program can only register no more than 6 event functions.
Example:
def on_button_a_pressed(): # define a function
print(“Button A is pressed!”)
codey.on_button_a_pressed() # register it to “when button A is pressed” event
on_button_a_pressed()/on_button_b_pressed()/on_button_c_pressed()
When the button is pressed, run the function.
def on_button_b_pressed():
print(“The B button is pressed”)
codey.on_button_b_pressed()
on_shaked()
When Codey is shaken, call the function.
def on_shaked():
print(“I’m shaken!”)
codey.on_shaked()
on_tilted_left()
Call the function when Codey tilts to the left.
def on_tilted_left():
print(“I’m tilted-left!”)
codey.on_tilted_left()
on_greater_than(volume, ‘sound_sensor’)
When the loudness is over a certain value, call the function.
def on_greater_than():
print(“The volume is over 50! Too loud!”)
codey.on_greater_than(50, ‘sound_sensor’)
on_less_than(lightness, ‘light_sensor’)
When the lightness is under a certain value, call the function.
def on_less_than():
print(“The light is under 30! too dark!”)
codey.on_less_than(30, ‘light_sensor’)
on_received(message_name)
When a Scratch broadcast is received, trigger the function.
def on_received():
print(“Game start!”)
codey.on_received(‘game_start’)
broadcast(message_name)
Broadcast a certain message to the Scratch system.
codey.broadcast(‘game_start’)
stop_all_scripts()/stop_this_script()/stop_other_scripts()
Stop all processes, this process, or other processes.
codey.stop_all_scripts() # stop all processes on Codey
Let the Rocky move
forward(speed, time)
Tell the Rocky to move forward for a certain period of time. If the time is not set, it will keep moving. The speed range is 0-100.
rocky.forward(50, 1) # run forward for 1 seconds at the speed of 50
rocky.forward(100) # run forward forever at the speed of 100
backward(speed, time)
Tell the Rocky to move backward for a certain period of time. If the time is not set, it will keep moving. The speed range is 0-100.
rocky.backward(50)
rocky.backward(100) # run backward at the max speed of 100
turn_right(speed, time)
Tell the Rocky to turn right for a certain period of time. If the time is not set, it will keep turning. The speed range is 0-100.
rocky.turn_right(50, 1) # turn right at speed 50 for 1 second
rocky.turn_right(100) # turn right at the max speed of 100
turn_left(speed, time)
Tell the Rocky to turn left for a certain period of time. If the time is not set, it will keep turning. The speed range is 0-100.
rocky.turn_left(50, 1) # turn left at speed 50 for 1 second
rocky.turn_left(100) # turn left at the max speed of 100
turn_right_by_degree(angle)
Make Rocky turn right at a certain angle until done.
rocky.turn_right_by_degree(90) # turn right for 90 degrees until done
turn_left_by_degree(angle)
Make Rocky turn left at a certain angle until done.
rocky.turn_left_by_degree(90) # turn left for 90 degrees until done
drive(left_speed, right_speed)
Set the speed of Codey’s two wheels at the same time.
rocky.drive(50, 50) # set the speed of both wheels to 50
stop()
Stop the movement of Codey
rocky.stop() # tell Codey to stop moving
Use Rocky’s Sensors and Light
color_ir_sensor.set_led_color(color)
Set the color of Rocky’s LED. Color can be one of: “red”, “green”, “blue”, “yellow”, “purple”, “cyan”, “white”, “black”. Set the color to “black” will turn off Rocky’s LED.
rocky.color_ir_sensor.set_led(“red”)
rocky.color_ir_sensor.set_led(“black”)
color_ir_sensor.is_obstacle_ahead()
Tell if there is obstacle ahead. Return True or False. (Rocky’s sensor array must face forward)
print(rocky.color_ir_sensor.is_obstacle_ahead())
color_ir_sensor
Get the value of the base sensor array.
- color_ir_sensor.get_light_strength(): get the ambient light intensity of the environment; return 0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_light(): get the reflection light value of the surface; return 0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_infrared(): get the IR reflection value of the surface; return 0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_greyness(): get the greyness of the surface by light sensor; return 0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_red(): get the red value of the surface; return 0-255
- color_ir_sensor.get_green(): get the green value of the surface; return 0-255
- color_ir_sensor.get_blue(): get the blue value of the surface; return 0-255
- color_ir_sensor.is_color(color_str): Tell whether the color sensor senses the specific color; return True or False. The color_name could be one of “red”, “green”, “blue”, “yellow”, “purple”, “cyan”, “white”, “black”.
print(“Lightness and Reflection: “, color_ir_sensor.get_light_strength(), color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_light())
print(“IR light value: “, color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_infrared())
print(“Greyness: “, color_ir_sensor.get_greyness())
print(“RGB value: “, color_ir_sensor.get_red(), color_ir_sensor.get_green(), color_ir_sensor.get_blue())
print(“On a red surface? “, color_ir_sensor.is_color(“red”))
Communicate with Infrared Signals
Codey can send and receive infrared signals.
ir_send(message)
send a piece of string message with Codey’s Infrared Emitter. Another Codey can receive this message with its Infrared Receiver.
codey.ir_send(“A”)
ir_receive()
When a piece of message sent with infrared signals is received, return a string value.
codey.show(codey.ir_receive())
