How Can We Help?
Python API
Python API
This article includes the following python API for Codey Rocky:
- Python API for Codey:refers to some API for Codey Rocky’s onboard driver.
- Python API for Rocky:API on Codey which used for control the Rocky to move or to receive dates send from sensors on Rocky.
- Python API for third-party libraries:some build-in interface for third-party libraries of Codey Rocky, such as mqtt or urequest.
- Python API for extension Neuron modules:API which may used when add Neuron modules to Codey Rocky.
Python API for Codey
led — Onboard RGB LED
Function
led.show(r, g, b)
Set the displayed color of the RGB LED, parameters:
- r refers to the value of red component, parameter range is 0 ~ 255,0 with no red component and 255 the highest red component.
- g refers to the value of green component, parameter range is 0 ~ 255,0 with no green component and 255 the highest green component.
- b refers to the value of blue component, parameter range is 0 ~ 255,0 with no blue component and 255 the highest blue component.
led.set_red(val)
Set the red color value of the RGB LED, parameters:
- val refers to the value of red component, parameter range is 0 ~ 255,0 with no red component and 255 the highest red component.
led.set_green(val)
Set the green color value of the RGB LED, parameters:
- val refers to the value of green component, parameter range is 0 ~ 255,0 with no green component and 255 the highest green component.
led.set_blue(val)
Set the blue color value of the RGB LED, parameters:
- val refers to the value of blue component, parameter range is 0 ~ 255,0 with no blue component and 255 the highest blue component.
led.off()
Turn off the RGB LED.
Sample Code:
import codey
import time
codey.led.show(255,255,255)
time.sleep(2)
codey.led.off()
time.sleep(2)
while True:
codey.led.set_red(255)
time.sleep(1)
codey.led.set_green(255)
time.sleep(1)
codey.led.set_blue(255)
time.sleep(1)
codey.led.off()
time.sleep(1)
display — Face Panel
Face Panel Introduction
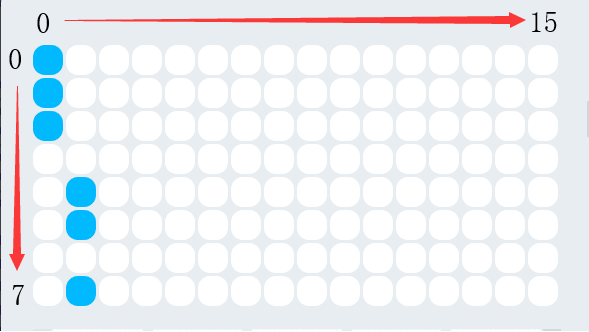
As shown in the figure above, the face panel has the upper left corner as the coordinate 0 point, and the direction of x and y is indicated by the arrow. About parameters displayed, take above figure as an example. The upper three of the first column data are lit and the data is converted to 11100000, that is, hexadecimal 0xe0.The second column verse is converted to 00001101, that is, In hexadecimal 0x0d. All the lattices in the above figure are converted to e00d0000000000000000000000000000.
Function
display.show_image(image, pos_x = 0, pos_y = 0, time_s = None)
Display custom dot matrix graphics as image parameters, parameters:
- image string data, each column of the dot matrix has 8 display points, which is 1 byte of data, converted to a hexadecimal string. Therefore, 16 columns of lattices need to be represented by 32 string data.
- pos_x displays the offset of the x-axis of the graph on the panel. The parameter range is -15 ~ 15, It starts from the 0 position as default if this parameter is not set.
- pos_y displays the offset of the graph on the y-axis of the panel. The parameter range is -7 ~ 7, It starts from the 0 position as default if this parameter is not set.
- time_s displays the time in seconds (in seconds). If this parameter is not set, the display remains unchanged until there is a clear screen or resetting the panel operation.
display.show(var, pos_x = 0, pos_y = 0, wait = True)
Display data in full-type data parameters, parameters:
- var full type, where the display of numeric and time types is treated specially, and the time format display needs to satisfy: [x]x:[x]x format (regular expression d?d:dd?)
- pos_x displays the offset of the data on the x-axis of the panel. The parameter range is -15 ~ 15. It starts from the 0 position as default if this parameter is not set.
- pos_y displays the offset of the data on the y-axis of the panel. The parameter range is -7 ~ 7. It starts from the 0 position as default if this parameter is not set.
- wait sets whether to block the display, where True: means blocking until the display is complete, False: means display but not blocking.
display.set_pixel(pos_x, pos_y, status)
Set the brightness and deactivation status of a single pixel of the panel, Parameters:
- pos_x The coordinates of the x-axis for the pixel on the panel. The parameter range is 0 ~ 15.
- pos_y The coordinates of the y-axis for the pixel on the panel. The parameter range is 0 ~ 7.
- status Boolean value,where True indicates that the pixel is lit, and False: indicates that the pixel is off.
display.get_pixel(pos_x, pos_y)
Get the current on and off states of a single pixel on the panel. The return value is a Boolean value, where True: indicates that the pixel is lit, and False: indicates that the pixel is off, parameter:
- pos_x The coordinates of the x-axis for the pixel on the panel. The parameter range is 0 ~ 15.
- pos_y The coordinates of the y-axis for the pixel on the panel. The parameter range is 0 ~ 7.
display.toggle_pixel(pos_x, pos_y)
Toggle the current on and off states of a single pixel on the panel, parameter:
- pos_x The coordinates of the x-axis for the pixel on the panel. The parameter range is 0 ~ 15.
- pos_y The coordinates of the y-axis for the pixel on the panel. The parameter range is 0 ~ 7.
display.clear()
Turn off all the LED lights on the display.
Sample Code:
import codey
import time
codey.display.show(“ffffff”)
codey.display.show(“123”)
time.sleep(1)
codey.display.show(“12345”, 3, 1)
codey.display.set_pixel(1, 1, True)
image = “ffffffffff000000000000000000000000”
codey.display.show_image(image, pos_x = 3, pos_y = 4)
time.sleep(1)
codey.display.clear()
print(“[1, 1]:”, codey.display.get_pixel(1, 1))
codey.display.show(“12:28”)
while True:
codey.display.toggle_pixel(7, 2)
codey.display.toggle_pixel(7, 4)
time.sleep(1)
speaker — Onboard Speaker
Function
speaker.stop_sounds()
Stop all sounds.
speaker.play_melody(file_name)
Playing an audio file, the function will not block when playing, but if it is called continuously, the next playback will stop the previous playback, Parameters:
- file_name String type, the audio file name of the wav format burned in Codey Rocky flash. When inputting, the format suffix .wav can also be omitted.
The optional sound file has:
hello.wav : hello
hi.wav : hi
bye.wav : bye
yeah.wav : yeah
wow.wav : wow
laugh.wav : laugh
hum.wav : hum
sad.wav : sad
sigh.wav : sigh
annoyed.wav : annoyed
angry.wav : angry
surprised.wav : scared
yummy.wav : pettish
curious.wav : curious
embarrassed.wav : embarrassed
ready.wav : ready
sprint.wav : sprint
sleepy.wav : snore
meow.wav : meow
start.wav : start
switch.wav : switch
beeps.wav : beeps
buzzing.wav : buzz
exhaust.wav : air-out
explosion.wav : explosion
gotcha.wav : gotcha
hurt.wav : painful
jump.wav : jump
laser.wav : laser
level up.wav : level-up
low energy.wav : low-energy
metal clash.wav : metal-clash
prompt tone.wav : prompt-tone
right.wav : right
wrong.wav : wrong
ring.wav : ringtone
score.wav : score
shot.wav : shot
step_1.wav : step_1
step_2.wav : step_2
wake.wav : activate
warning.wav : warning
speaker.play_melody_until_done(file_name)
The audio file is played until it stops, and the function blocks playback, that is, the next instruction cannot be executed until the sound is played, parameter:
- file_name String type, the audio file name of the wav format burned in Codey Rocky flash. When inputting, the format name .wav can also be omitted. For specific optional parameters, see play_melody.
speaker.play_note(note_num, beat = None)
Play note, digital note definitions please refer to: scratch digital note descriptionfor()Beats(block)), prameters:
- note_num numeric value, range of values 48 – 72, or string type, such as C4.
- beat value data, indicates the number of beats, the default value is always playing.
notes and frequency is as follows:
[‘C2′,’65’], [‘D2′,’73’], [‘E2′,’82’], [‘F2′,’87’],
[‘G2′,’98’], [‘A2′,’110’], [‘B2′,’123’], [‘C3′,’131’],
[‘D3′,’147’], [‘E3′,’165’], [‘F3′,’175’], [‘G3′,’196’],
[‘A3′,’220’], [‘B3′,’247’], [‘C4′,’262’], [‘D4′,’294’],
[‘E4′,’330’], [‘F4′,’349’], [‘G4′,’392’], [‘A4′,’440’],
[‘B4′,’494’], [‘C5′,’523’], [‘D5′,’587’], [‘E5′,’659’],
[‘F5′,’698’], [‘G5′,’784’], [‘A5′,’880’], [‘B5′,’988’],
[‘C6′,’1047’], [‘D6′,’1175’], [‘E6′,’1319’], [‘F6′,’1397’],
[‘G6′,’1568’], [‘A6′,’1760’], [‘B6′,’1976’], [‘C7′,’2093’],
[‘D7′,’2349’], [‘E7′,’2637’], [‘F7′,’2794’], [‘G7′,’3136’],
[‘A7′,’3520’], [‘B7′,’3951’], [‘C8′,’4186’], [‘D8′,’4699’],
speaker.play_tone(frequency, time = None)
Play the setting frequency sound, parameters:
- frequency Numerical data, the frequency of sound which is played, and its value range is 0 ~ 5000.
- time Numerical data, indicating the playback time (in milliseconds – ms) and its value range is 0 ~ the value range limit.
speaker.rest(number)
Stop the beat, parameters:
- number Numerical data, the number of paused beats, its value range is 0 ~ the value range limit.
Constant
speaker.volume
Numerical data, the property value of the volume, you can modify or read this value. Modify this value to control the volume. Its value range is 0 ~ 100.
speaker.tempo
Numerical data, indicating the nature of the playback speed, in bmp (beat per minute), which is the length of each beat.Its value range is 6 ~ 600. The default value is 60, which means that the duration of one beat is 1 second. The beats of the rest and play_note functions are affected by this constant.
Sample Code:
import codey
import time
codey.speaker.play_melody(“hello”, True)
codey.display.show(“hello”)
codey.display.clear()
codey.speaker.play_note(48, 1)
codey.speaker.rest(1)
codey.display.show(“note”)
codey.display.clear()
codey.speaker.play_note(“C4”, 1)
codey.speaker.rest(1)
codey.display.show(“C4”)
codey.display.clear()
codey.speaker.play_tone(1000, 2)
codey.speaker.rest(1)
codey.display.show(“tone”)
codey.display.clear()
print(“tempo:”, end = “”)
print(codey.speaker.tempo)
codey.speaker.play_note(“C4”, 1)
codey.speaker.rest(1)
codey.speaker.tempo = 120
codey.speaker.volume = 20
codey.speaker.play_note(“C4”, 1)
codey.speaker.rest(1)
sound_sensor — Onboard Sound Sensor
Function
sound_sensor.get_loudness()
Get the sound intensity detected by the sound sensor, and the return value is the volume. The value range is 0 ~ 100.
Sample Code:
import codey
while True:
codey.display.show(codey.sound_sensor.get_loudness())
light_sensor — Onboard Light Sensor
Function
light_sensor.get_value()
Get the light intensity detected by the light sensor, and the return value is the intensity value of visible light. The value range is 0 ~ 100.
Sample Code:
import codey
while True:
codey.display.show(codey.light_sensor.get_value())
potentiometer — Onboard Potentiometer
Function
potentiometer.get_value()
Get the current value of the potentiometer knob. The value range is 0 ~ 100.
Sample Code:
import codey
while True:
codey.display.show(codey.potentiometer.get_value())
button_a — Onboard Button A
Function
button_a.is_pressed()
Get the current state of button A. The result returned is True: the button is pressed, or the False: button is not pressed.
Sample Code:
import codey
def loop():
while True:
if codey.button_a.is_pressed():
print(“button A is pressed”)
loop()
button_b — Onboard Button B
Function
button_b.is_pressed()
Get the current state of button B. The result returned is True: the button is pressed, or the False: button is not pressed.
Sample Code:
import codey
def loop():
while True:
if codey.button_b.is_pressed():
print(“button B is pressed”)
loop()
button_c — Onboard Button C
Function
button_c.is_pressed()
Get the current state of button C. The result returned is True: the button is pressed, or the False: button is not pressed.
Sample Code:
import codey
def loop():
while True:
if codey.button_c.is_pressed():
print(“button C is pressed”)
loop()
motion_sensor — Onboard Motion Sensor
Motion Sensor Introduction
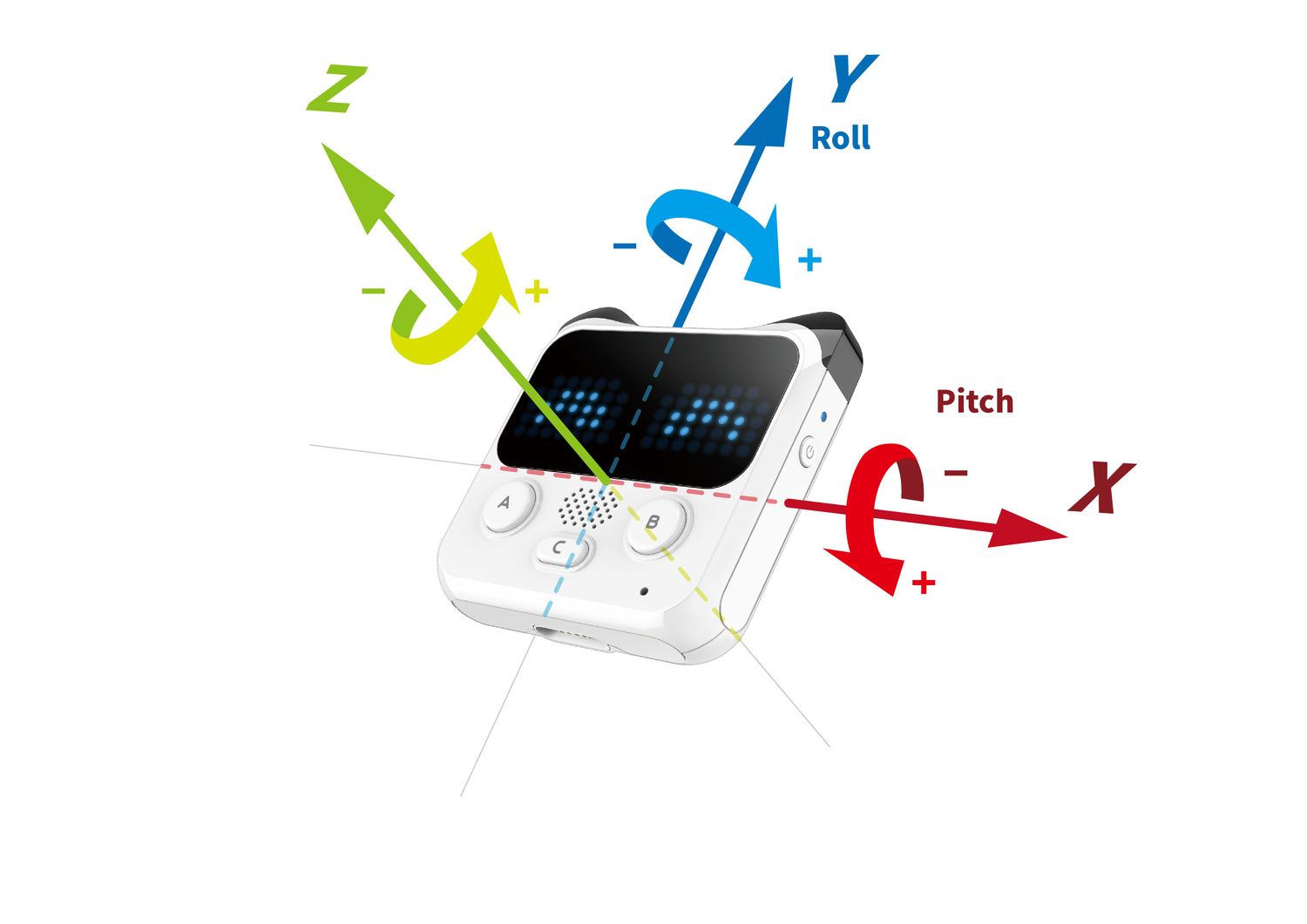
As shown in the picture above, the direction of the roll and pitch are based on the right-handed screw rule.
Both roll and pitch are 0° when the Codey is horizontally placed.
- Roll range: -90° ~ 90°
- Pitch range: -180 ° ~ 180 °
Function
motion_sensor.get_roll()
Get the roll of the Euler angle, the returned data range is -90 ~ 90.
motion_sensor.get_pitch()
Get the pitch of the Euler angle, the returned data range is -180 ~ 180.
motion_sensor.get_yaw()
Get the yaw of the Euler angle, The returned data range is 0 ~ 360. Since the Codey onboard sensor is a six-axis sensor, there is no electronic compass. So in fact the yaw angle is just the integral of the Z-axis angular velocity. It has accumulated errors. If you want to get a true yaw angle, this API is not suitable for use.
motion_sensor.get_rotation(axis)
Get the angle at which the Codey rotates on the three axes, and the counterclockwise direction is the positive direction, parameter:
- axis String type, with x, y, z representing the axis defined by Codey.
motion_sensor.reset_rotation(axis = “all”)
The current angle of initial rotation around the three axes is 0, and the get_rotation() will start at 0, parameter:
- axis string type, with x, y, z representing the axis defined by Codey, and all representing all three axes. This is also the default value for this function.
motion_sensor.is_shaked()
Check if the Codey is shaken, the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that Codey is shaken, and False means that Codey is not shaken.
motion_sensor.get_shake_strength()
If the Codey is shaken, this function can obtain the intensity of the shaking. The value of the return value range is 0 ~ 100. The larger the value, the greater the intensity of the shaking.
motion_sensor.is_tilted_left()
Check if Codey is tilted to the left, and the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that Codey is tilted to the left, and False means that Codey is not tilted to the left.
motion_sensor.is_tilted_right()
Check if Codey is tilted to the right, and the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that Codey is tilted to the right, and False means that Codey is not tilted to the right.
motion_sensor.is_ears_up()
Check if the ear of Codey is up, the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that the ear of Codey is facing up, and False means that the ear of Codey is not facing up.
motion_sensor.is_ears_down()
Check if the ear of Codey is down, the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that the ear of Codey is facing down, and False means that the ear of Codey is not facing down.
motion_sensor.is_display_up()
Check if the face panel of Codey is up, the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that the panel of Codey is facing up, and False means that the panel of Codey is not facing up.
motion_sensor.is_display_down() Check if the face panel of Codey is down, the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that the panel of Codey is facing down, and False means that the panel of Codey is not facing down.
motion_sensor.is_upright()
Check if Codey is upright, the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that Codey is upright, and False means that Codey is not upright.
motion_sensor.get_acceleration(axis)
Get the acceleration values of the three axes in m/s^2, Parameters:
- axis String type, with x, y, z representing the axis defined by Codey.
motion_sensor.get_gyroscope(axis)
Get the angular velocity values of the three axes in °/sec, Parameters:
- axis String type, with x, y, z representing the axis defined by Codey。
Sample Code 1:
import codey
import time
while True:
roll = codey.motion_sensor.get_roll()
pitch = codey.motion_sensor.get_pitch()
yaw = codey.motion_sensor.get_yaw()
print(“roll:”, end = “”)
print(roll, end = “”)
print(” ,pitch:”, end = “”)
print(pitch, end = “”)
print(” ,yaw:”, end = “”)
print(yaw)
time.sleep(0.05)
Sample Code 2:
import codey
while True:
if codey.motion_sensor.is_shaked():
print(“shake_strength:”, end = “”)
print(codey.motion_sensor.get_shake_strength())
Sample Code 3:
import codey
while True:
if codey.motion_sensor.is_tilted_left():
print(“tilted_left”)
if codey.motion_sensor.is_tilted_right():
print(“tilted_right”)
if codey.motion_sensor.is_ears_up():
print(“ears_up”)
if codey.motion_sensor.is_ears_down():
print(“ears_down”)
if codey.motion_sensor.is_display_up():
print(“display_up”)
if codey.motion_sensor.is_display_down():
print(“display_down”)
if codey.motion_sensor.is_upright():
print(“upright”)
ir — Onboard Infrared Transceiver
Function
ir.receive()
Returns the string information received by the infrared receiver, so the data sent by the infrared sender must end with \n. If it is a remote control command that receives the NEC encoding protocol, use another function receive_remote_code().
ir.receive_remote_code()
Get the date from infrared remote controller. The data contains two parts: address and content, so it returns a list data which length 2. The first parameter is the address code, and the latter parameter is the data code.
ir.send(str)
Send infrared string, parameters:
- str The string data to be emitted, the function send will add the \n terminator at the end of the string automatically.
ir.start_learning()
Start infrared learning and only support remote control commands that learn the standard NEC protocol.
ir.stop_learning()
Stop infrared learning.
ir.save_learned_result(index)
Save the learned infrared coding result to the corresponding area, parameters:
- index the value range is 0 ~ 15, a total of 16 storage areas.
ir.send_learned_result(index = 1)
Send infrared learning saved infrared code, the learning result of the area with index = 1 is set as default, parameters:
- index The index value range is 0 ~ 15, a total of 16 storage areas.
ir.learn(time = 3)
Infrared learning time seconds, after calling this API will save the infrared information learned in time seconds. Default saved to the area with index = 1, parameter:
- time learning time, in seconds.
Sample Code 1:
import codey
import event
@event.start
def start_cb():
print(“start event succeeded”)
while True:
codey.display.show(codey.ir.receive_remote_code()[1])
Sample Code 2:
import codey
import event
@event.button_a_pressed
def button_a_cb():
print(“button a event succeeded”)
codey.ir.learn()
codey.led.show(0, 100, 0)
@event.button_b_pressed
def button_a_cb():
print(“button b event succeeded”)
while True:
codey.ir.send_learned_result()
@event.button_c_pressed
def button_c_cb():
print(“button b event succeeded”)
while True:
codey.display.show(codey.ir.receive())
wifi — Onboard Wi-Fi
Function
wifi.start(ssid = “wifi_ssid”, password = “password”, mode = codey.wifi.STA)
Start wifi connection, the API will not block process, API exit does not mean that wifi is connected, you need to call wifi.is_connected() to judge, Parameter:
- ssid string type, Wi-Fi account.
- password string type, Wi-Fi password.
- mode starts the Wi-Fi mode.
wifi.is_connected()
Check if Wi-Fi is connected, the return value is Boolean, where True means that wifi has established a connection, False means that wifi has not yet established a connection.
Constant
wifi.STA
The Wi-Fi station mode, that is, the wireless adapter mode. In this mode, wifi can be connected to the router.
wifi.AP
Wireless access point mode, the general wireless routing / bridge works in this mode. In this mode, it allows other wireless devices to access.
wifi.APSTA
The Wi-Fi AP and STA modes coexist.
Sample Code:
import codey
codey.wifi.start(‘makeblock’, ‘password’, codey.wifi.STA)
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
while True:
if codey.wifi.is_connected():
codey.led.show(0,0,255)
else:
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
battery — Built-in Lithium Battery
Function
battery.get_voltage()
Get the current battery voltage, the return value is a floating point data. The unit is V.
battery.get_percentage()
Get the percentage of remaining battery power. The return value is an integer. The data range is 0 ~ 100, where 100 means there is still 100% of the remaining battery.
Sample Code:
import codey
while True:
print(“vol” + str(codey.battery.get_voltage()))
print(“percentage” + str(codey.battery.get_percentage()))
codey_timer — Counter
Function
codey.get_timer()
Gets the current value of the timer (the timer runs from the time the user script starts), the return value is a floating point data. The unit is seconds.
codey.reset_timer()
Initialize the value of the timer.
Sample Code:
import codey
codey.reset_timer()
while True:
print(“time:”, end = “”)
print(codey.get_timer())
codey_broadcast — Broadcast Module
Function
codey.broadcast(str)
A broadcast can be sent to the serial port, Bluetooth, and its own event monitoring unit, Parameter:
- str The content of the broadcast.
Sample Code:
import codey
import event
@event.button_a_pressed
def button_a_cb():
print(“button a event succeeded”)
codey.broadcast(“hello”)
@event.received(“hello”)
def received_cb():
print(“received message: hello”)
codey_external_module_detect — External Module Access Detection
Function
codey.has_neuron_connected()
Check whether there is any neuron module connected to Codey, and the return value is a Boolean value, where True indicates that the neuron module is connected to Codey (including the connecting of the Rocky), and False indicates that there is no neuron module connected to the Codey.
codey.is_rocky_connected()
Check if the Rocky is connected to the Codey, the return value is a Boolean value, where True means that there is a Rocky connected to the Codey, and False means no Rocky connected to Codey.
Sample Code:
import codey
import time
while True:
if codey.is_rocky_connected():
print(“rocky is in”)
else:
print(“rocky is out”)
time.sleep(1)
codey_script_control — Script/Thread Control
Function
codey.stop_this_script()
Stop the current script, consistent with the scratch stop script feature.
codey.stop_other_scripts()
Stop other scripts, consistent with the scratch stop other scripts feature.
codey.stop_this_script()
Stop all scripts, consistent with the scratch stop all scripts.
Sample Code:
import codey
import time
import event
@event.start
def start_cb():
while True:
print(“start cb executing…”)
time.sleep(1)
print(“stop this script”)
codey.stop_this_script()
@event.button_a_pressed
def button_a_cb():
codey.stop_other_scripts()
while True:
print(“button a event”)
@event.button_b_pressed
def button_b_cb():
codey.stop_other_scripts()
while True:
print(“button b event”)
@event.button_c_pressed
def button_c_cb():
codey.stop_all_scripts()
event — Event Processing Unit
Event Processing Unit Introduction
The way user events are used currently supports two ways of writing. One is registration:
import codey
import time
import event
def start_cb():
while True:
codey.led.show(255, 0, 0)
time.sleep(1)
codey.led.show(0, 0, 0)
time.sleep(1)
event.start(start_cb)
The other is to use a decorator, such as:
import codey
import time
import event
@event.start
def start_callback():
while True:
codey.led.show(255, 0, 0)
time.sleep(1)
codey.led.show(0, 0, 0)
time.sleep(1)
Function
event.start(callback)
Startup event.
event.shaked(callback)
Codey was shaken event.
event.received(callback, msgstr)
Broadcast reception detection event. In addition to the callback parameter, the parameter:
- msgstr string type, the string to be matched. The event will be triggered when the received string matches the matching string.
event.button_a_pressed(callback)
Button A pressed event.
event.button_b_pressed(callback)
Button B pressed event.
event.button_c_pressed(callback)
Button C pressed event.
event.tilted_left(callback)
Codey left-tilted event.
event.tilted_right(callback)
Codey right-tilted event.
event.ears_up(callback)
Codey ears-up event.
event.ears_down(callback)
Codey ears-down event.
event.ir_received(callback, ir_str)
Infrared string reception detection event. In addition to the callback parameter, the parameter:
- ir_str string type, the string to be matched. The event will be triggered when the received string matches the matching string.
event.greater_than(callback, threshold, type_str)
The threshold comparison event, which will be triggered when the threshold is exceeded. In addition to the callback parameter, the parameter:
- threshold value data, set the threshold for triggering.
- type_str string data, currently only supports sound_sensor: volume sensor, timer: timer.
event.less_than(callback, threshold, type_str)
Threshold comparison event, triggered below the threshold, in addition to the callback parameter, the parameter:
- threshold value data, set the threshold for triggering
- type_str string data, currently only supports light_sensor: light sensor.
Sample Code:
import codey
import event
@event.button_a_pressed
def button_a_cb():
print(“button a event triggered”)
@event.button_b_pressed
def button_b_cb():
print(“button b event triggered”)
@event.button_c_pressed
def button_c_cb():
print(“button c event triggered”)
@event.greater_than(20, “sound_sensor”)
def sound_sensor_cb():
print(“sound sensor greater event triggered”)
@event.greater_than(5, “timer”)
def timer_cb():
print(“timer greater event triggered”)
@event.less_than(30, “light_sensor”)
def light_sensor_cb():
print(“light sensor event triggered”)
Python API for Rocky
motion – Rocky Chassis Movement
Function
rocky.stop()
Rocky stops moving.
rocky.forward(speed, t = None, straight = False)
Rocky moves forward, parameters:
- speed The value of motion speed, parameter range is -100 ~ 100, negative numbers represent backwards, positive numbers represent forward.
- t The value of the motion time, in seconds, the parameter range is 0 ~ the value range limit. If set to 1, it means the rocky will move forward for 1s. If this parameter is not set, the forward state is maintained until there is the motion stop command or new motion command.
- straight Enable the gyro sensor to correct the forward direction or not. If this parameter is not set, it is not enabled by default.
rocky.backward(speed, t = None, straight = False)
Rocky moves backward, parameters:
- speed The value of motion speed, parameter range is -100 ~ 100, negative numbers represent forward, positive numbers represent backward.
- t The value of the motion time, in seconds, the parameter range is 0 ~ the value range limit. If set to 1, it means the rocky will move backward for 1s. If this parameter is not set, the backward state is maintained until there is the motion stop command or new motion command.
- straight Enable the gyro sensor to correct the backward direction or not. If this parameter is not set, it is not enabled by default.
rocky.turn_left(speed, t = None)
Rocky turns left, parameters:
- speed The value of turn speed, parameter range is -100 ~ 100, negative numbers represent turn right, positive numbers represent turn left.
- t The value of the motion time, in seconds, the parameter range is 0 ~ the value range limit. If set to 1, it means the rocky will turn left for 1s. If this parameter is not set, the turn left state is maintained until there is the motion stop command or new motion command.
rocky.turn_right(speed, t = None)
Rocky turns right, parameters:
- speed The value of turn speed, parameter range is -100 ~ 100, negative numbers represent turn right, positive numbers represent turn left.
- t The value of the motion time, in seconds, the parameter range is 0 ~ the value range limit. If set to 1, it means the rocky will turn left for 1s. If this parameter is not set, the turn left state is maintained until there is the motion stop command or new motion command.
rocky.drive(left_power, right_power)
Rocky turns according to the set value for each motor, parameters:
- left_power Motor speed of left wheel, parameter range is -100 ~ 100, negative numbers represent the left wheel rotates backward, positive numbers represent the left wheel rotates forward.
- right_power Motor speed of right wheel, parameter range is -100 ~ 100, negative numbers represent the right wheel rotates backward, positive numbers represent the right wheel rotates forward.
rocky.turn_right_by_degree(angle, speed = 40)
Rocky turns right according to the set degree, parameters:
- angle Angle of rotation, negative numbers represent turn left, positive numbers represent turn right.
- speed Turning speed, parameter range is 0 ~ 100, if this parameter is not set, the default speed is 40. (Since the gyro sensor is used for turning specific angle, it is recommended not to modify the speed to avoid the turning angle being inaccurate).
rocky.turn_left_by_degree(angle, speed = 40)
Rocky turns left according to the set degree, parameters:
- angle Angle of rotation, negative numbers represent turn right, positive numbers represent turn left.
- speed Turning speed, parameter range is 0 ~ 100, if this parameter is not set, the default speed is 40. (Since the gyro sensor is used for turning specific angle, it is recommended not to modify the speed to avoid the turning angle being inaccurate).
Sample Code:
import codey
import rocky
import time
rocky.forward(50, 1)
rocky.stop()
rocky.backward(50, 1)
rocky.turn_left(50, 1)
rocky.turn_right(50, 1)
rocky.drive(50, 80)
time.sleep(2)
while True:
rocky.turn_right_by_degree(80, 40)
rocky.turn_right_by_degree(80, 20)
color_ir_sensor – Color IR Sensor
Color Infrared Sensor Introduction
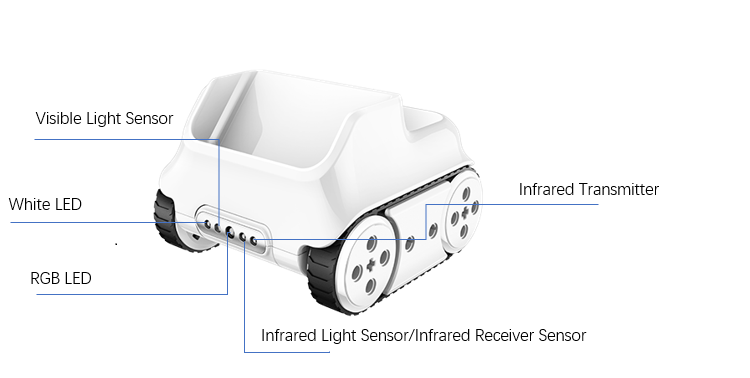
As shown in the figure, the sensors in front of the rocky are:
- White LED:light white to achieve detecting the visible light reflection intensity on the surface of the object with using visible light sensor.
- Visible Light Sensor:detect the visible light intensity.
- RGB LED:light LED with specific RGB value to achieve recognizing the color with using the visible light sensor.
- Infrared Light Sensor:detect the infrared light intensity
- Infrared Transmitter:transmit infrared light to achieve detecting the infrared light reflection intensity on the surface of the object with using the infrared light sensor.
Function
color_ir_sensor.get_red()
Get the size of the red color component of the color sensor, parameter range is 0 ~ 100.
color_ir_sensor.get_green()
Get the size of the green color component of the color sensor, parameter range is 0 ~ 100.
color_ir_sensor.get_blue()
Get the size of the blue color component of the color sensor, parameter range is 0 ~ 100.
color_ir_sensor.is_color(color_str)
Judge whether a matching color is detected, parameters:
- color_str color type, including red, green, blue, yellow, cyan, purple, white,black, the corresponding parameter is red, green, blue, yellow, cyan, purple, white, black. Return value is boolean, Ture represents color matching, False represents the colors do not match.
color_ir_sensor.get_light_strength()
Get the ambient light intensity d`etected by the visible light sensor, parameter range is 0 ~ 100.
color_ir_sensor.get_greyness()
Get the grayscale value detected by the visible light sensor (using RGB LED and visible light sensor), parameter range is 0 ~ 100.
color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_light()
Get the visible light reflection intensity detected by the visible light sensor, parameter range is 0 ~ 100.
color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_infrared()
Get the infrared light reflection intensity detected by the infrared light receiving tube, parameter range is 0 ~ 100.
color_ir_sensor.is_obstacle_ahead()
Detect if there are obstacles in front, the return value is boolean, Turerepresents obstacles, False represents no obstacles.
color_ir_sensor.set_led_color(color_name)
Set color for the RGB LED light of the color sensor, parameters:
- color_name including red, green, blue, yellow, cyan, purple, white, black, the corresponding parameter is red, green, blue, yellow, cyan, purple, white, black.
Sample Code:
import codey
import rocky
while True:
if rocky.color_ir_sensor.is_obstacle_ahead():
rocky.color_ir_sensor.set_led_color(‘white’)
else:
rocky.color_ir_sensor.set_led_color(‘black’)
Python API for Third-Party Libraries
urequests – Network Request Module
Function
urequests.request(method, url, data=None, json=None, headers={})
Send a network request, it will block the response data returned to the network, parameters:
- method method of establishing a network request. e.g. HEAD,GET,POST,PUT,PATCH, DELETE.
- url URL of the network request.
- data (optional), a dictionary, tuple list [(key, value)] (will be form coded), byte or class file object sent in the request body.
- json (optional), json data sent in the request body.
- headers (optional), HTTP header dictionary to be sent with the request.
urequests.head(url, **kw)
Send a HEAD request, the return type is the response of the request, parameters:
- url URL of the network request.
- **kw request optional parameters.
urequests.get(url, **kw)
Send a GET request, the return type is the response of the request, parameters:
- url URL of the network request.
- **kw request optional parameters.
urequests.post(url, **kw)
Send a POST request, the return type is the response of the request, parameters:
- url URL of the network request.
- **kw request optional parameters.
urequests.put(url, **kw)
Send a PUT request, the return type is the response of the request, parameters:
- url URL of the network request.
- **kw request optional parameters.
urequests.patch(url, **kw)
Send a PATCH request, the return type is the response of the request, parameters:
- url URL of the network request.
- **kw request optional parameters.
urequests.delete(url, **kw)
Send a DELETErequest, the return type is the response of the request, parameters:
- url URL of the network request.
- **kw request optional parameters.
Sample Code:1
import codey
import urequests as requests
import time
# Fill in your router’s ssid and password here.
codey.wifi.start(‘wifi_ssid’, ‘password’)
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
while True:
if codey.wifi.is_connected():
codey.led.show(0,0,255)
res = requests.get(url=’http://www.baidu.com/’)
print(res.text)
time.sleep(3)
else:
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
Sample Code:2
import codey
import urequests as requests
import time
# Fill in your router’s ssid and password here.
codey.wifi.start(‘wifi_ssid’, ‘password’)
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
hour = minite = second = “00”
while True:
if codey.wifi.is_connected():
try:
res = requests.get(url = ‘http://www.time.ac.cn/timeflash.asp?user=flash’).text
hour_begin = res.find(‘<hour>’) + len(‘<hour>’)
hour_end = res.find(‘</hour>’)
minite_begin = res.find(‘<minite>’) + len(‘<minite>’)
minite_end = res.find(‘</minite>’)
second_begin = res.find(‘<second>’) + len(‘<second>’)
second_end = res.find(‘</second>’)
if hour_begin > len(‘<hour>’) and hour_end > hour_begin and \
minite_begin > len(‘<minite>’) and minite_end > minite_begin and \
second_begin > len(‘<second>’) and second_end > second_begin:
if hour_end – hour_begin == 1:
hour = ‘0’ + res[hour_begin:hour_end]
elif hour_end – hour_begin == 2:
hour = res[hour_begin:hour_end]
if minite_end – minite_begin == 1:
minite = ‘0’ + res[minite_begin:minite_end]
elif minite_end – minite_begin == 2:
minite = res[minite_begin:minite_end]
if second_end – second_begin == 1:
second = ‘0’ + res[second_begin:second_end]
elif second_end – second_begin == 2:
second = res[second_begin:second_end]
print(hour + “:” + minite + “:” + second)
cur_time = hour + ‘:’ + minite;
codey.display.show(cur_time)
except:
print(“get error data”)
else:
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
Sample Code:3
import codey
import urequests as requests
import ujson
# user_account and password is mblock’s account and password
def get_user_request_header():
post_data = ujson.dumps({ ‘account’: ‘user_account’, ‘password’: ‘password’})
request_url = ‘http://passport2.makeblock.com/v1/user/login’
res = requests.post(request_url, headers = {‘content-type’: ‘application/json’}, data = post_data).json()
header_data = ”
if res[‘code’] == 0:
header_data = { “content-type”: ‘application/json; charset=utf-8’, “devicetype”: ‘1’}
header_data[“uid”] = str(res[‘data’][‘user’][‘uid’])
header_data[“deviceid”] = ’30AEA427EC60′
return header_data
# Get weather information
# cid: checkpoint id
# arg: Information to be queried
# aqi: Air Quality Index
# pm25: PM2.5 concentration
# pm10: PM10 concentration
# co: Carbon monoxide concentration
# so2: Sulfur dioxide concentration
# no2: Nitrogen dioxide concentration
def get_air_quality_info(cid, arg):
if not codey.wifi.is_connected():
return ”
post_data = ujson.dumps({ “cid”: cid, “arg”: arg})
request_url = ‘http://msapi.passport3.makeblock.com/’ + ‘air/getone’
res = requests.post(request_url, headers = get_user_request_header(), data = post_data)
text = res.text
return float(text)
# Fill in your router’s ssid and password here.
codey.wifi.start(‘wifi_ssid’, ‘password’)
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
while True:
if codey.wifi.is_connected():
codey.led.show(0,0,255)
data = get_air_quality_info(‘1539′,’aqi’) #1539 is Shenzhen checkpoint id
codey.display.show(data)
else:
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
mqtt – Message Queue Telemetry Transmission
Class
class mqtt.MQTTClient(client_id, server, port=0, user=None, password=None, keepalive=0, ssl=False, ssl_params={}) Instantiating the interface object of MQTT client, parameters:
- client_id the unique client id string used when connecting to the broker. If client_id is zero length or None, then one will be randomly generated. In this case, the parameter clean_session of the connect function must be True.
- server The host name or IP address of the remote server.
- port (optional), the network port of the server host to connect to. The default port number is 1883. Please note that the default port number of the MQTT over SSL/TLS is 8833.
- user (optional), the username registered on the server.
- password (optional), the password registered on the server.
- keepalive (optional), the client’s keepalive time out value. Default is 60 s.
- ssl (optional), whether enable the SSL/TLS support.
- ssl_params (optional), SSL/TLS parameter.
connect(clean_session=True)
Connect the client to the server, this is a blocking function, parameters:
- clean_session a boolean that determines the client type. If True, the broker will remove all information about this client when it disconnects. If False, the client is a durable client and subscription information and queued messages will be retained when the client disconnects.
reconnect()
Reconnect to the server using the details provided previously. You must call connect before calling this function.
disconnect()
Disconnect from the server.
ping()
Test the connectivity between the server and client.
set_last_will(topic, msg, retain=False, qos=0)
Set the will to be sent to the server. If the client disconnects without calling disconnect(), the server will post a message on its behalf, parameters:
- topic The topic of the will post.
- msg A will message to send.
- retain If set to True, the will message will be set to the last known good/reserved message for the topic.
- qos Is used for the quality of service level of the will.
publish(topic, msg, retain=False, qos=0)
A message is sent from the client to the agent and then sent from the agent to any client that subscribes to the matching topic, parameters:
- topic The topic of the message should be posted.
- msg The actual message to send.
- retain If set to True, the will message will be set to the last known good/reserved message for the topic.
- qos The level of quality of service to use.
subscribe(topic, qos=0)
Subscribe to a topic of the service, this module provides some helper functions to subscribe and process messages directly. For example set_callback, parameters:
- topic The subject of the message to subscribe.
- qos The level of quality of service to use.
set_callback(f)
Sets the callback function for the topic subscription, which is called when the server responds to our subscription request, parameters:
- f callback function.
wait_msg()
Wait for the server until the server has no pending messages. This function is a blocking function.
check_msg()
Check if the server has pending messages. If not, return directly, if any, do same processing as function wait_msg.
Sample Code:
from mqtt import MQTTClient
import codey
import time
MQTTHOST = “mq.makeblock.com”
MQTTPORT = 1883
# Fill in as you like
client_id = “20180911203800”
# Example Path
Topic = “/sensors/temperature/#”
mqttClient = MQTTClient(client_id, MQTTHOST, port=MQTTPORT, user=’test’, password=’test’, keepalive=0, ssl=False)
# Connect to the MQTT server
def on_mqtt_connect():
mqttClient.connect()
# publish a message
def on_publish(topic, payload, retain=False, qos = 0):
mqttClient.publish(topic, payload, retain, qos)
# message processing function
def on_message_come(topic, msg):
print(topic + ” ” + “:” + str(msg))
codey.display.show(msg)
# subscribe message
def on_subscribe():
mqttClient.set_callback(on_message_come)
mqttClient.subscribe(Topic, qos = 1)
# Fill in your router’s ssid and password here.
codey.wifi.start(‘wifi_ssid’, ‘password’)
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
codey.display.show(0)
while True:
if codey.wifi.is_connected():
on_mqtt_connect()
on_subscribe()
codey.led.show(0,0,255)
while True:
# Blocking wait for message
on_publish(“/sensors/temperature/home”, str(38), qos = 1)
mqttClient.wait_msg()
time.sleep(1)
else:
codey.led.show(0,0,0)
